
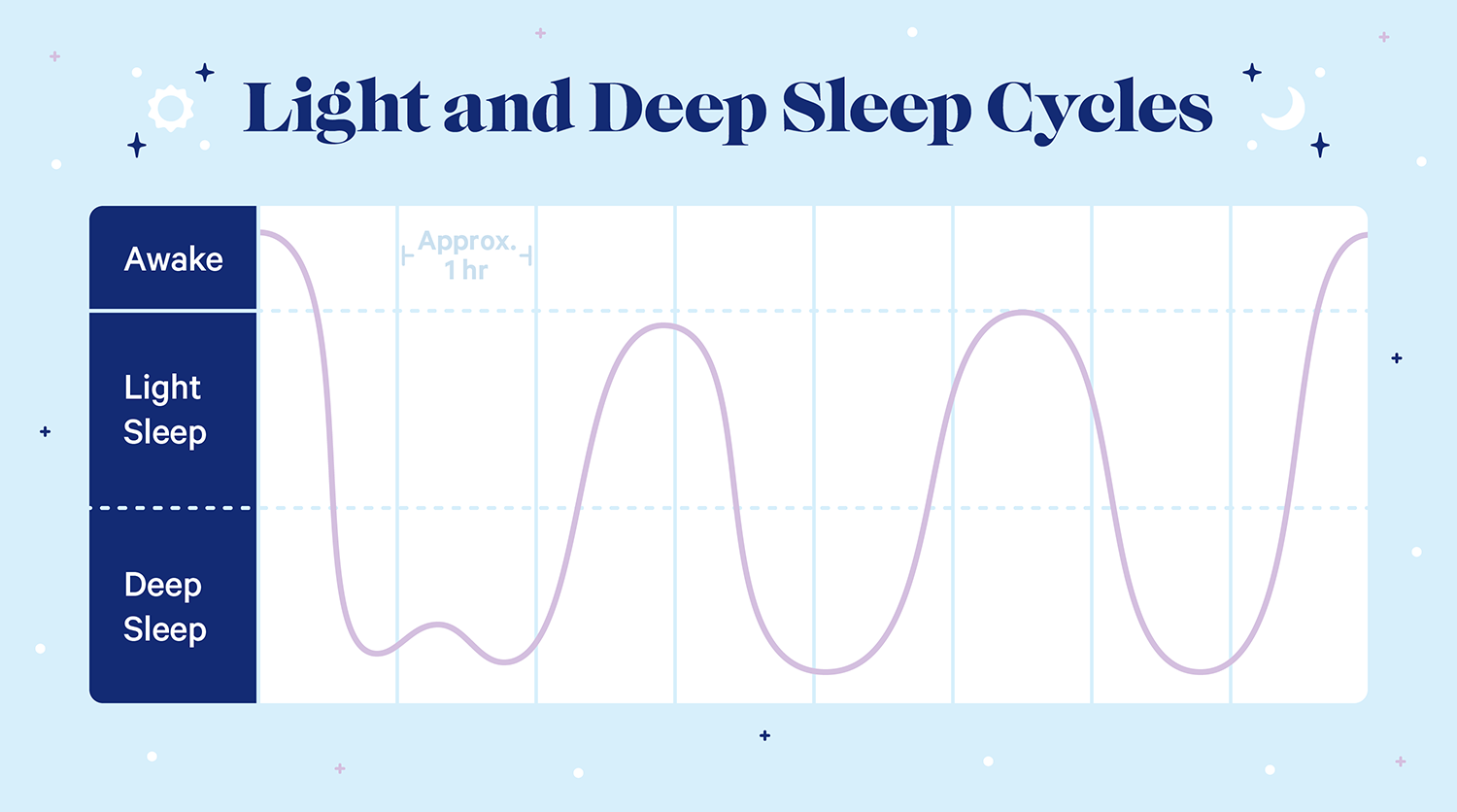
The REM stage also involves an increase in brain activity, breathing, and heart rate. tonic REM sleep, which doesn’t involve these eye movements.phasic REM sleep, during which your eyes will move rapidly in short bursts.You can think of Stage R as the BOGO sleep stage, since it involves two separate phases: This stage of sleep is where dreams happen. You won’t wake easily from this stage of sleep. brain and body processes important for health and well-being, like tissue repair and memory consolidation.While you may not wake up quite so easily as you might during N1 sleep, it’s still fairly easy to be woken up during this sleep stage.

You’ll spend most of your time asleep in this stage. Next is the “light sleep” stage, the one you enter before reaching deep sleep. You might wake up easily, often without knowing you had already fallen asleep. This first and lightest stage of sleep involves: You can consider this stage the “falling asleep” stage. Here’s what goes on during these periods of sleep. Deeper, longer REM sleep usually happens near the morning. When you sleep, you cycle through all stages of NREM and REM sleep several times. Experts have further split NREM into three distinct substages: N1, N2, and N3. There’s rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. First, a quick rundown on the stages of sleep


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
